Three‐Dimensional Turbulence‐Resolving Simulations of the Plunge Phenomenon in a Tilted Channel
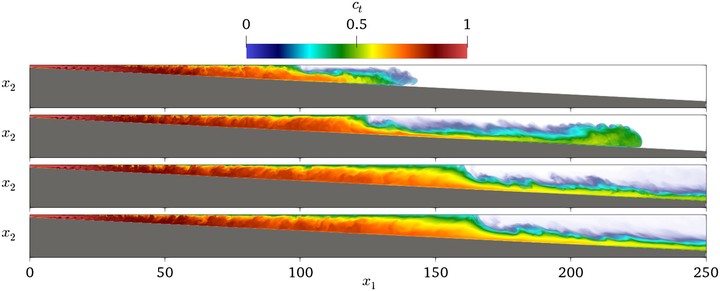 Side view of the total concentration field for case 4 in the test section, for dimensionless time equals to 500, 1,000, 3,000, and 5,000 from top to bottom, respectively. Source: Schuch et al. (2018).
Side view of the total concentration field for case 4 in the test section, for dimensionless time equals to 500, 1,000, 3,000, and 5,000 from top to bottom, respectively. Source: Schuch et al. (2018).Abstract
Abstract Hyperpycnal flows are produced when the density of a fluid flowing in a relatively quiescent basin is greater than the density of the fluid in the basin. The density differences can be due to the difference in temperatures, salinity, turbidity, concentration, or a combination of them. When the inflow momentum diminishes, the inflowing fluid eventually plunges under the basin fluid and flows along the bottom floor as an underflow density current. In the present work, 3-D turbulence-resolving simulations are performed for an hyperpycnal flow evolving at the bottom floor of a tilted channel. Using advanced numerical techniques designed for supercomputers, the incompressible Navier-Stokes and transport equations are solved to reproduce numerically the experiments of Lamb et al. (2010) obtained inside a flume with a long tilted ramp. This study focuses on presenting and validating a new numerical framework for the correct reproduction and analysis of the plunge phenomenon and its associated flow features. A very good agreement is found between the experimental data of Lamb et al. (2010), the analytical models of Parker and Toniolo (2007), and the present turbulence-resolving simulations. The mixing process between the ambient fluid and the underflow density current is also analyzed thanks to visualizations of vortical structures at the interface.